Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Abe, Shinichiro
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 65(5), p.326 - 330, 2023/05
, 65(5), p.326 - 330, 2023/05
Non-destructive faults (the so-called soft errors) in microelectronics caused by environmental radiation such as neutrons and muons have been recognized as a serious reliability problem. The number of microelectronics requiring high reliability increases with the growth of the information society. Therefore, it is not realistic to evaluate the soft error rate (SER) of all microelectronics by measurement. Moreover, the evaluation of SER in the pre-manufacturing stage is sometimes required. As a result, the evaluation of SER by simulation become more important. We have developed the soft error simulation method with PHITS code. We have also simulated the neutron- and muon-induced soft errors. These results will be reported in the journal of the Atomic Energy Society of Japan (AESJ) as the explanatory article.
Liao, W.*; Ito, Kojiro*; Abe, Shinichiro; Mitsuyama, Yukio*; Hashimoto, Masanori*
IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 68(6), p.1228 - 1234, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:31.78(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Secondary cosmic-ray neutron-induced single event upset (SEU) is a cause of soft errors on micro electronic devices. Multiple cell upsets (MCUs) are particularly serious problems since it is difficult to recover MCUs. In this study, we have performed irradiation tests of neutrons on 65-nm bulk SRAM at the national metrology institute of Japan (NMIJ) in Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST) and measured SEU cross sections and MCU cross sections to investigate the effect on neutrons with the energies below 10 MeV on soft errors. It was found that SEU cross sections change drastically around 6 MeV. The proportion of MCU to total events does not change very much over the wide range of neutron energy. We also analyzed the total soft error rate (SER) of SEU and MCU by folding the neutron energy-dependent cross section and the flux spectra of the terrestrial neutron at New York and Tokyo. The calculated result indicates that the SER originating from the low-energy neutrons below 10 MeV is mostly negligible in the terrestrial environment.
Liao, W.*; Hashimoto, Masanori*; Manabe, Seiya*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Abe, Shinichiro; Tampo, Motonobu*; Takeshita, Soshi*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*
IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 67(7), p.1566 - 1572, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Muon-induced single event upset (SEU) is predicted to increase with technology scaling. The angle of incidence of terrestrial muons is not always perpendicular to the chip surface. Consequently, the impact of the angle of incidence of muons on SEUs should be evaluated. This study conducts negative muon irradiation tests on bulk SRAM and FDSOI SRAM at two angles of incidence: 0 degree (vertical) and 45 degree (tilted). The tilted incidence drifts the muon energy peak to a higher energy. Moreover, the SEU characteristics (i.e., such as the voltage dependences of the SEU cross sections and multiple cells upset patterns) between the vertical and tilted incidences are similar.
Abe, Shinichiro; Liao, W.*; Manabe, Seiya*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Hashimoto, Masanori*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*
IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 66(7, Part 2 ), p.1374 - 1380, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:61.94(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Single event upsets (SEUs) caused by secondary cosmic-ray neutrons have recognized as a serious reliability problem for microelectronic devices. Acceleration tests at neutron facilities are convenient to validate soft error rates (SERs) quickly, but some corrections caused from measurement conditions are required to derive realistic SERs at actual environment or to compare other measured data. In this study, the effect of irradiation side on neutron-induced SEU cross sections was investigated by performing neutron transport simulation using PHITS. SERs for 65-nm bulk CMOS SRAMs are estimated using the sensitive volume model. It was found from simulation that SERs for the sealant side irradiation are 30-50% larger than those for the board side irradiation. This difference comes from the difference of production yield and angular distribution of secondary H and He ions, which are the main cause of SEUs. Thus the direction of neutron irradiation should be reported when the result of acceleration tests are published. This result also indicates that SERs can be reduced by equipping device with sealant side facing downward.
Liao, W.*; Hashimoto, Masanori*; Manabe, Seiya*; Abe, Shinichiro; Watanabe, Yukinobu*
IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 66(7), p.1390 - 1397, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:82.61(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Multiple-cell upset (MCU) in static random access memory (SRAM) is a major concern in radiation effects on microelectronic devices since it can spoil error correcting codes. Neutron-induced MCUs have been characterized for terrestrial environment. On the other hand, negative muon-induced MCUs were recently reported. Neutron- and negative muon-induced MCUs are both caused by secondary ions, and hence, they are expected to have some similarity. In this paper, we compare negative muon- and neutron-induced MCUs in 65-nm bulk SRAMs at the irradiation experiments using spallation and quasi-monoenergetic neutrons and monoenergetic negative muons. The measurement results show that the dependencies of MCU event cross section on operating voltage are almost identical. The Monte Carlo simulation is conducted to investigate the deposited charge. The distributions of deposited charge obtained by the simulation are consistent with the above-mentioned experimental observations.
Manabe, Seiya*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Liao, W.*; Hashimoto, Masanori*; Nakano, Keita*; Sato, Hikaru*; Kin, Tadahiro*; Abe, Shinichiro; Hamada, Koji*; Tampo, Motonobu*; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 65(8), p.1742 - 1749, 2018/08
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:62.99(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Recently, the malfunction of microelectronics caused by secondary cosmic-ray muon is concerned as semiconductor devices become sensitive to radiation. In this study, we have performed muon irradiation testing for 65-nm ultra-thin body and thin buried oxide (UTBB-SOI) SRAMs in the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), in order to investigate dependencies of single event upset (SEU) cross section on incident muon momentum and supply voltage. It was found that the SEU cross section by negative muon are approximately two to four times larger than those by positive muon in the momentum range from 35 MeV/c to 39 MeV/c. The supply voltage dependence of muon-induced SEU cross section was measured with the momentum of 38 MeV/c. SEU cross sections decrease with increasing supply voltage, but the decreasing of SEU cross section by negative muon is gentler than that by positive muon. Experimental data of positive and negative muon irradiation with the momentum of 38 MeV/c were analyzed by PHITS. It was clarified that the negative muon capture causes the difference between the SEU cross section by negative muon and that by positive muon.
Liao, W.*; Hashimoto, Masanori*; Manabe, Seiya*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Abe, Shinichiro; Nakano, Keita*; Sato, Hikaru*; Kin, Tadahiro*; Hamada, Koji*; Tampo, Motonobu*; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 65(8), p.1734 - 1741, 2018/08
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:81.7(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Soft error induced by secondary cosmic-ray muon is concerned since susceptibility of semiconductor device to soft error increases with the scaling of technology. In this study, we have performed irradiation tests of muons on 65-nm bulk CMOS SRAM in the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) and measured soft error rate (SER) to investigate mechanism of muon-induced soft errors. It was found that SER by negative muon increases above 0.5 V supply voltage, although SER by positive muon increases monotonically as the supply voltage lowers. SER by negative muon also increases with forward body bias. In addition, negative muon causes large multiple cell upset (MCU) of more than 20 bits and the ratio of MCU events to all the events is 66% at 1.2V supply voltage. These tendencies indicate that parasitic bipolar action (PBA) is highly possible to contribute to SER by negative muon. Experimental data are analyzed by PHITS. It was found that negative muon can deposit larger charge than positive muon, and such events that can deposit large charge may trigger PBA.
Abe, Shinichiro; Sato, Tatsuhiko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(3), p.451 - 458, 2016/03
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:64.88(Nuclear Science & Technology)Secondary cosmic-ray neutron-induced soft errors have been recognized as a serious problem affecting the reliability of microelectronic devices. Our developed Multi-scale Monte Carlo simulator called PHYSERD is a reliable code for analysis of soft error. However, PHYSERD takes long computational time to calculate processes of collecting charges because event-by-event technology computer-aided design (TCAD) simulation is time consuming. In this study, the multiple sensitive volume (MSV) model is adopted to estimate collected charge. Secondary cosmic-ray neutron-induced soft errors in an NMOSFET are analyzed based on the MSV model using PHITS. The results are compared with those obtained by PHYSERD based on event-by-event TCAD simulation and by single sensitive volume (SSV) model using PHITS. It is found that PHITS+MSV provides approximate SERs in a shorter time than PHYSERD. Furthermore, PHITS+MSV reproduces SERs and collected charges more accurately than PHITS+SSV by considering the spatial dependence of the charge collection efficiencies.
Laird, J. S.; Hirao, Toshio; Onoda, Shinobu; Ito, Hisayoshi
IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 52(5), p.1504 - 1512, 2005/10
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:44.9(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)no abstracts in English
Onoda, Shinobu; Hirao, Toshio; Laird, J. S.; Okamoto, Tsuyoshi*; Koizumi, Yoshiharu*; Kamiya, Tomihiro
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 231(1-4), p.497 - 501, 2005/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:30.27(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Yamakawa, Takeshi; Hirao, Toshio; Abe, Hiroshi; Onoda, Shinobu; Wakasa, Takeshi; Shibata, Toshihiko*; Kamiya, Tomihiro
JAERI-Review 2004-025, TIARA Annual Report 2003, p.19 - 20, 2004/11
no abstracts in English
Laird, J. S.; Hirao, Toshio; Onoda, Shinobu; Wakasa, Takeshi; Yamakawa, Takeshi; Abe, Hiroshi; Oyama, Hidenori*; Kamiya, Tomihiro
JAERI-Review 2004-025, TIARA Annual Report 2003, p.14 - 16, 2004/11
no abstracts in English
 n diodes due to heavy ion irradiation
n diodes due to heavy ion irradiationHirao, Toshio; Laird, J. S.; Onoda, Shinobu; Shibata, Toshihiko*; Wakasa, Takeshi; Yamakawa, Takeshi; Abe, Hiroshi; Takahashi, Yoshihiro*; Onishi, Kazunori*; Ito, Hisayoshi
Proceedings of the 6th International Workshop on Radiation Effects on Semiconductor Devices for Space Application (RASEDA-6), p.105 - 109, 2004/10
no abstracts in English
Abe, Tetsuo*; Onishi, Kazunori*; Takahashi, Yoshihiro*; Hirao, Toshio
Proceedings of the 6th International Workshop on Radiation Effects on Semiconductor Devices for Space Application (RASEDA-6), p.157 - 160, 2004/10
no abstracts in English
Kuboyama, Satoshi*; Ikeda, Naomi*; Hirao, Toshio; Matsuda, Sumio*
Proceedings of the 6th International Workshop on Radiation Effects on Semiconductor Devices for Space Application (RASEDA-6), p.165 - 168, 2004/10
no abstracts in English
Onoda, Shinobu; Hirao, Toshio; Laird, J. S.; Wakasa, Takeshi; Yamakawa, Takeshi; Okamoto, Tsuyoshi*; Koizumi, Yoshiharu*; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Ito, Hisayoshi
Proceedings of the 6th International Workshop on Radiation Effects on Semiconductor Devices for Space Application (RASEDA-6), p.173 - 176, 2004/10
no abstracts in English
Hirao, Toshio; Laird, J. S.; Onoda, Shinobu; Wakasa, Takeshi; Ito, Hisayoshi
Proceedings of the 6th International Workshop on Radiation Effects on Semiconductor Devices for Space Application (RASEDA-6), p.187 - 189, 2004/10
no abstracts in English
Wakasa, Takeshi; Hirao, Toshio; Sanami, Toshiya*; Onoda, Shinobu; Abe, Hiroshi; Tanaka, Susumu; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Okamoto, Tsuyoshi*; Ito, Hisayoshi
Proceedings of the 6th International Workshop on Radiation Effects on Semiconductor Devices for Space Application (RASEDA-6), p.213 - 216, 2004/10
no abstracts in English
Kamiya, Tomihiro; Hirao, Toshio; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 219-220, p.1010 - 1014, 2004/06
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:48.81(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
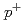 -
-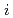 -
-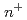 photodiodes studied by pulsed laser measurements
photodiodes studied by pulsed laser measurementsLaird, J. S.; Hirao, Toshio; Onoda, Shinobu; Ito, Hisayoshi
IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 50(6, Part1), p.2003 - 2010, 2003/12
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:56.43(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)no abstracts in English